Cramping, abdominal pain, bloating and changes in bowel habits (diarrhea or constipation) are the main symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. It’s not known what causes it, but IBS is common and affects up to 15 percent of the population to some extent. The good news is that IBS usually doesn’t lead to more serious diseases and can be controlled with lifestyle changes, diet and medicines.과민성대장증후군한의원
When you see your doctor, explain all of your symptoms, including when they started and how long they’ve been going on. You’ll also want to discuss any “red flag” symptoms that you think may signal a more serious problem.
Your doctor will probably look at your health history and do a physical exam. Your doctor will ask you questions about your family’s health, too. They’ll also do tests to make sure there is nothing else that could be causing your symptoms, such as a blood test for inflammation and stool tests for signs of other digestive tract problems.
Treatment for IBS includes diet, exercise, over-the-counter and prescription medications, herbal remedies and psychotherapy. Your doctor will work with you to find a treatment that works best for your symptoms and your situation. They might even recommend that you try a few different treatments to see what helps.
If your IBS is caused by stress, a number of psychological techniques have been shown to help. These include cognitive behavioral therapy, which is when you talk to a trained mental health professional who helps you change the ways that you think and act in response to stressors; gut-directed psychotherapy, which is when your therapist focuses on relieving stress on the brain-gut axis; and relaxation training.
Many people with IBS find that their symptoms improve with dietary modification. For example, some people with diarrhea can get relief by reducing the amount of caffeine and fatty foods they eat. Other people might find relief by adding fiber to their diets. Your doctor will recommend the type of fiber that’s right for you, such as psyllium or methylcellulose.
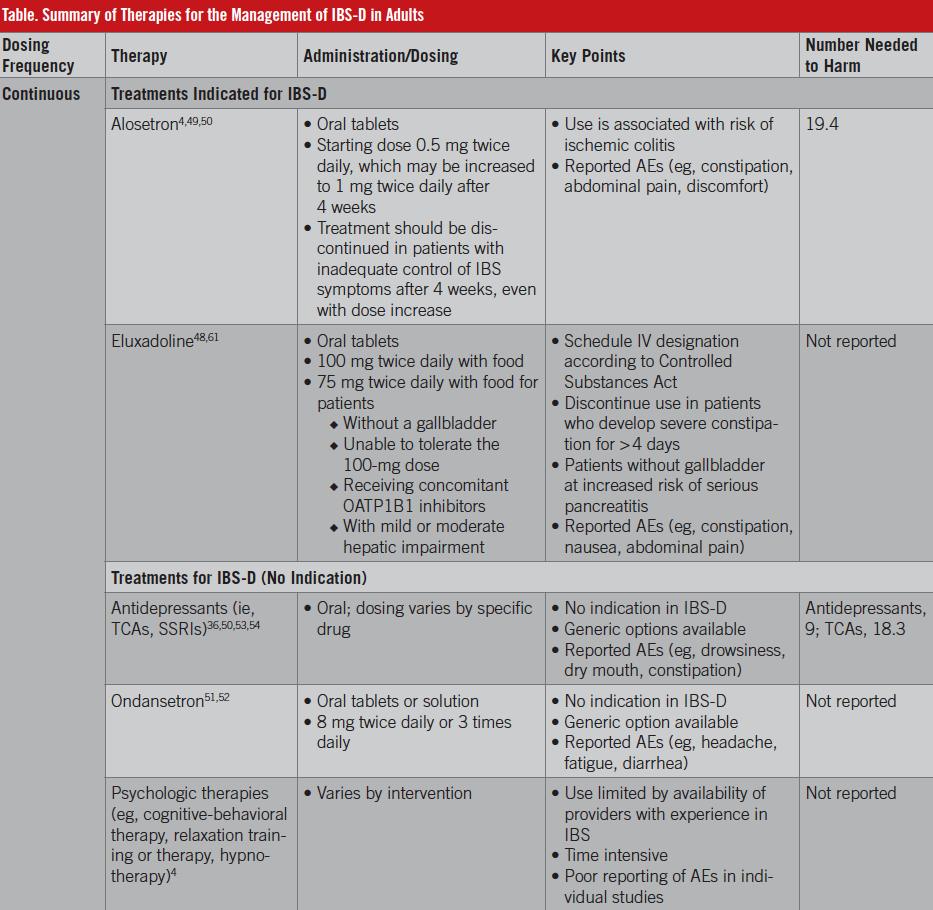
Antidiarrheal drugs are often used to treat IBS-related diarrhea. They slow gut transit and decrease intestinal secretion, which may reduce watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Examples of antidiarrheal medications include Imodium, loperamide and eluxadoline.
Many people with IBS who are taking a combination of over-the-counter and prescription medication find that it helps control their IBS. But it’s important to tell your doctor about any herbal remedies and over-the-counter medications you’re taking before starting a new one, because they might interact with each other. You might also want to discuss a supplement that contains probiotics, which may help reduce the severity of your IBS symptoms. In some cases, your doctor might recommend acupuncture. It’s not clear exactly how acupuncture works, but it might be that stimulating certain points on the body affects how your digestive tract functions. You might also try hypnosis or psychotherapy. Studies have shown that hypnosis and psychotherapy can help relieve IBS-related anxiety and depression.해우소한의원
